Sleep Apnea
SLEEP APNEA
WHAT IS SLEEP APNEA?
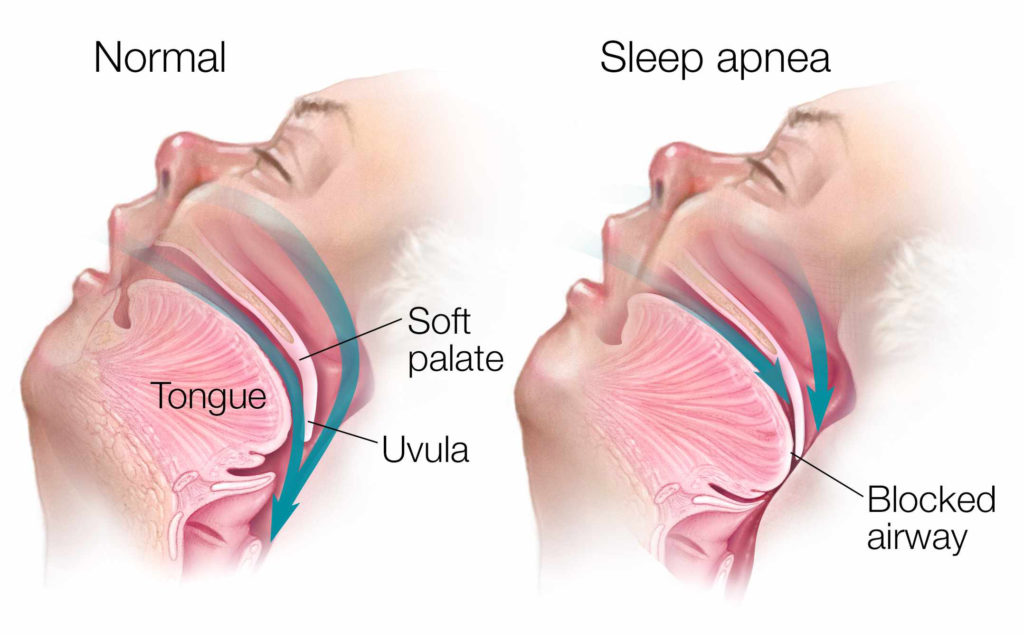
Sleep apnea is a potentially serious sleep disorder in which breathing is briefly interrupted during sleep. This pause could last at least ten seconds. Sleep apnea can be divided in two:
- Obstructive sleep apnea: Occurs when the muscles of the throat fail to keep the airway open, causing fragmented sleep.
- Central sleep apnea: The brain fails to properly control breathing during sleep.
Obstructive sleep apnea is more common than central sleep apnea.
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF SLEEP APNEA?
Sleep apnea can affect anyone at any age or ethnicity, but there are a number of factors that increase risk:
- Excess weight
- Having a small upper airway
- Small jaw, recessed chin or a large neck size (17 inches or greater in men and 16 inches or greater in women).
- Having large tongue, tonsils or uvula.
- Smoking habits
- Use of alcohol, sedatives or tranquilizers
- Age 40 and older
- Family history of sleep apnea
WHAT ARE THE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF SLEEP APNEA?
The most common signs and symptoms of obstructive and central sleep apnea include:
- Interrupted sleep, it would be mainly notified by another person (partner, friend, parents)
- Loud snoring
- Gasping for air during sleep
- Dry mouth in the morning
- Morning headache
- Insomnia
- Poor performance in everyday activities.
- Irritability
WHAT COMPLICATIONS ARE RELATED TO SLEEP APNEA?
Sleep apnea is a serious medical condition. If left untreated, complications can include:
- High blood pressure or heart problems: Sudden drops in blood oxygen levels that occur during sleep increase blood pressure.
- Stroke: It may also increase your risk of recurrent heart attack.
- Metabolic syndrome: Altogether with sleep apnea, it is linked to a higher risk of heart disease.
- Liver problems: Persons with sleep apnea are likely to show nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Depression
- Diabetes: Increase risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Medications and surgery: People with sleep apnea are more likely to have complications after major surgery due to general anesthesia or sedation.
- Sleep-deprived partners
**If you have heart disease, multiple episodes of low blood oxygen can lead to sudden death.
WHAT ARE THE TREATMENTS FOR SLEEP APNEA?
You may be able to treat slight sleep apnea with some lifestyle changes:
- Lose weight
- Avoid alcohol consumption
- Quit smoking
- Lay on the side instead of the back when you sleep.
Other appliances or methods for treating sleep apnea:
- Dental appliances which reposition lower jaw and tongue.
- CPAP: A mask that blows air during sleep in order to keep it open during sleep.
- Surgery for sleep apnea
- Somnoplasty
- Medication, among others.
WHEN TO SEE A DOCTOR?
If you suspect you may have sleep apnea, the first thing to do is see your doctor.
WHAT ARE THE POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS OF SCALING AND ROOT PLANING?
The possible complications are minimal. You may be at risk of infection after the procedure, so your dentist may prescribe an antibiotic or special mouthwash to use for a few days.
You may also experience pain and tenderness in gums for a few days following the procedure.